Women in sport
Introduction
The first modern Olympic Games were held in 1896 in Athens, Greece. However, only men were permitted to compete. It was considered by Olympic organisers that the inclusion of women would be ‘impractical, uninteresting, unaesthetic and incorrect’.
Four years later, at the 1900 Paris Games, women were only permitted to compete in limited events: lawn tennis, golf, croquet and sailing. In subsequent games, the restrictions on women competitors have been progressively relaxed.
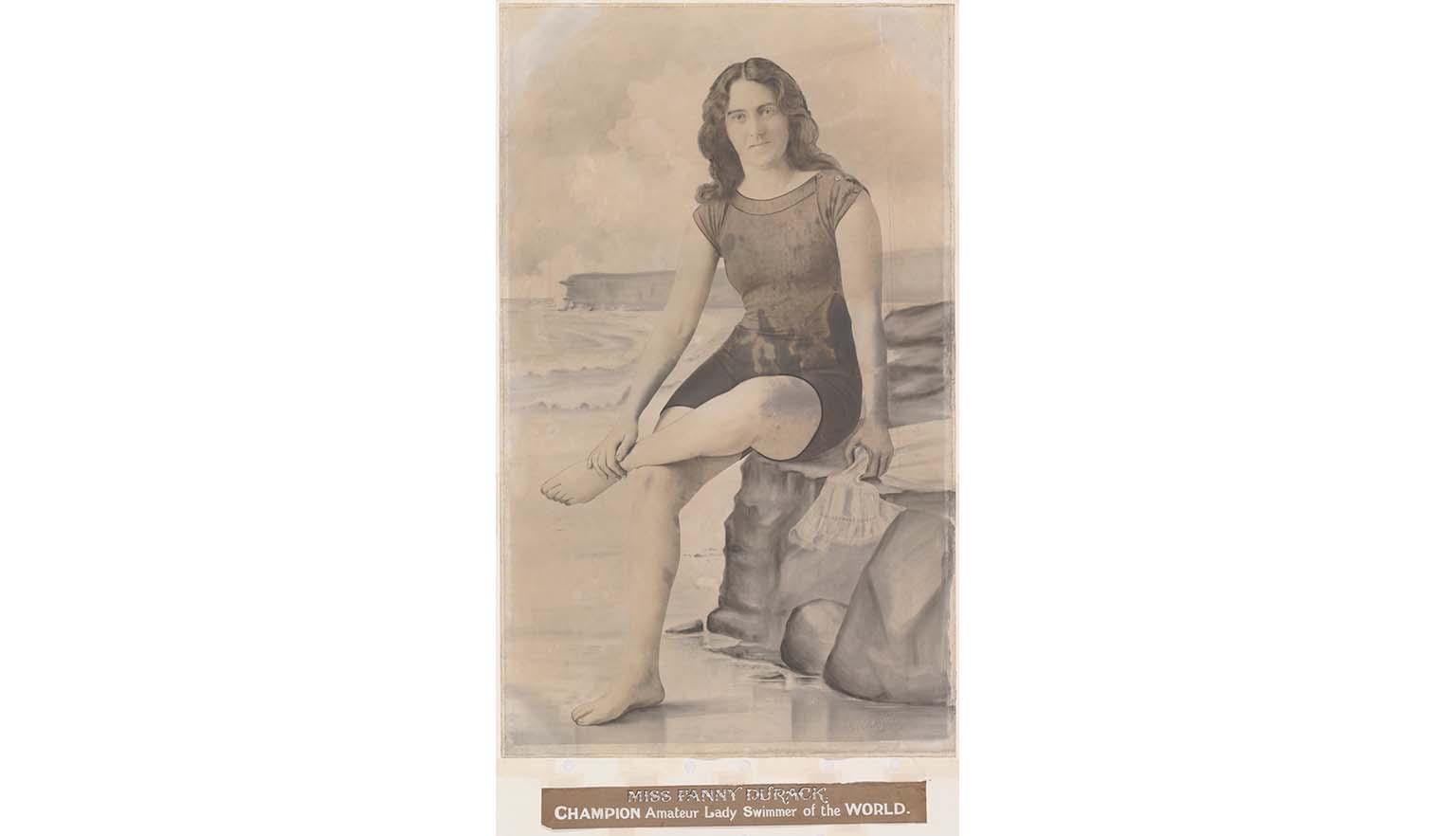
Trailblazer Franny Durak
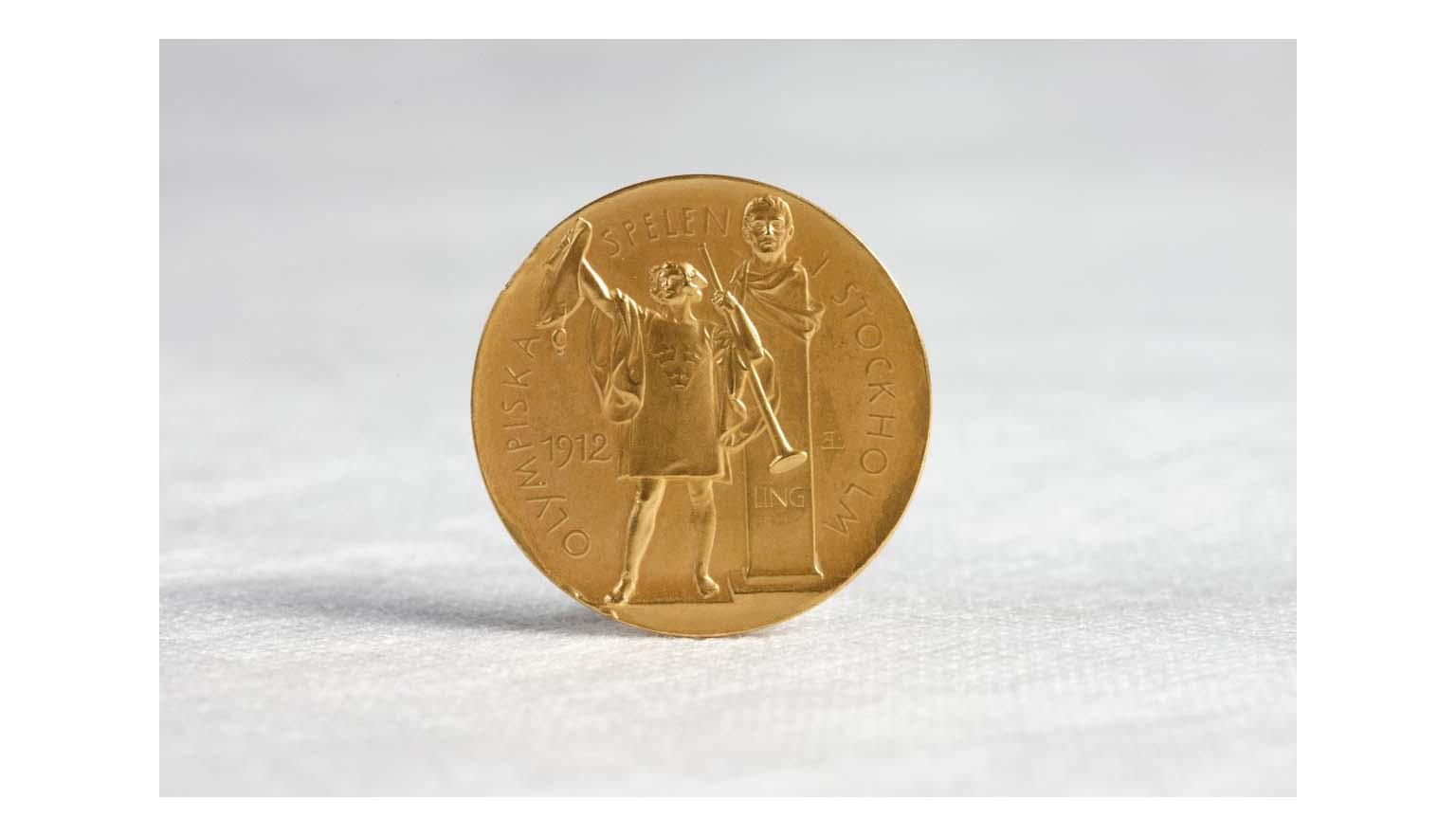
Despite laws saying that women couldn’t swim in mixed company - which means they couldn’t swim where men could see them - Fanny Durack became the first Australian to win a gold medal at an international swimming competition and the first woman to win a gold medal for swimming at an Olympic Games.
She took gold at the 1912 Stockholm Olympics where she set a world record and, from 1910 to 1918, she was the record holder for all swimming events from 100 metres to the mile marathon.
Women's sport in Australia
In Australia, women also faced restrictions on how, where and when they could take part in sport, both as competitors and for recreation.
In colonial times, women were encouraged only to play sports that did not challenge gender stereotypes — sports such as croquet and lawn bowls were popular during this time.
From the late 1800s until the early 20th century, swimming was especially restricted for women. They were not permitted to swim in male company, could access beaches and public pools only at designated times, and were required to wear loose-fitting, heavy swimsuits to ‘protect them’ from the gaze of men. During the 1920s and 1930s, more practical swimwear was allowed.
In 1900, the first female-only sporting groups were formed. Most were lawn bowls or golf clubs, but by the 1930s, athletics and track and field clubs for women were also established.
From the 1970s, male-only and female-only sporting groups began to merge. In 2017, Cricket Australia (CA) and the Australian Cricketers' Association (ACA) reached a deal to ensure all Australian cricketers, regardless of gender, would receive equal pay on signing.
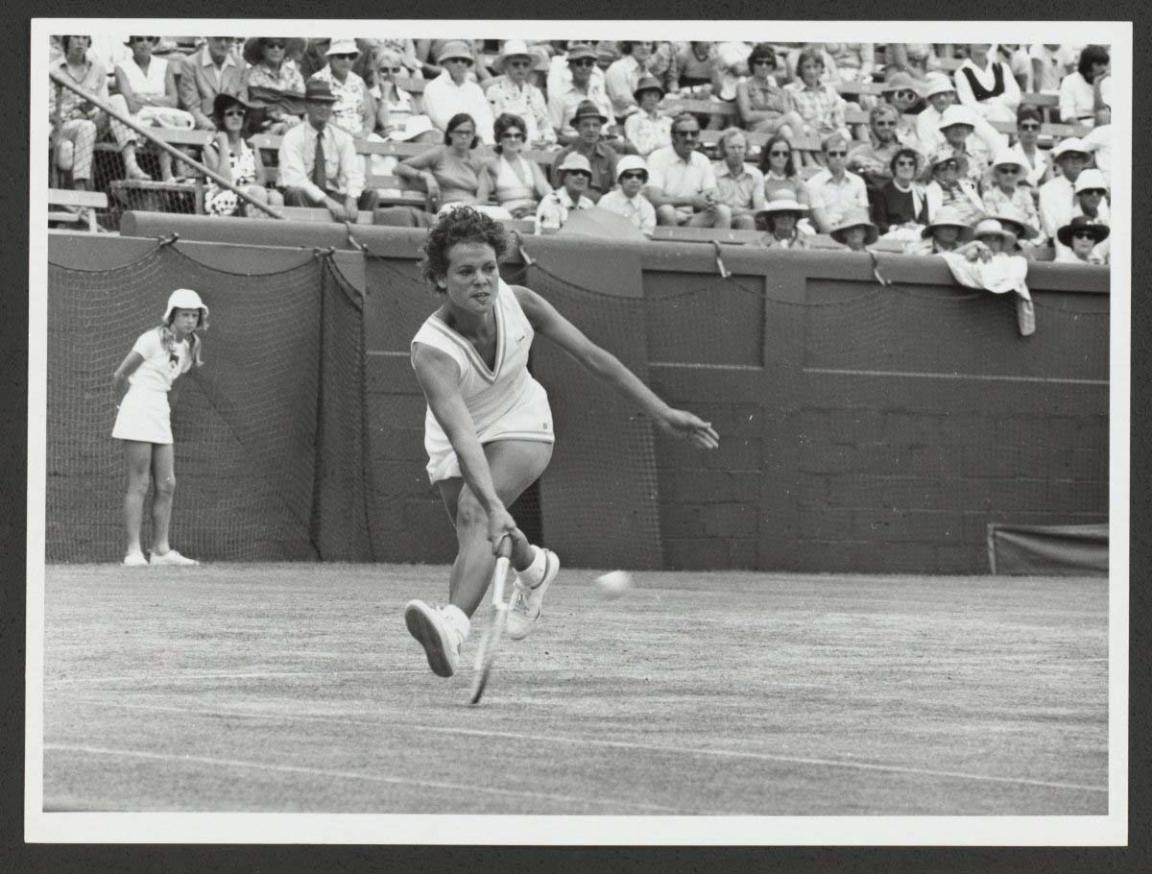

Don Edwards & Australian Information Service, Evonne Goolagong playing in the Australian Open Tennis Championships, Melbourne, 1 January 1967, nla.gov.au/nla.obj-137405043
Don Edwards & Australian Information Service, Evonne Goolagong playing in the Australian Open Tennis Championships, Melbourne, 1 January 1967, nla.gov.au/nla.obj-137405043
Inequality continues
Despite the relaxation of rules segregating competitors by gender, inequality persists in the sporting world.
As of 2012, there were still 39 Olympic events not open to women. Inequality also continues in areas such as funding and media coverage.
A 2010 study showed that of all sport-related coverage in the Australian media, only 9% related to women’s sport. The lack of coverage has made it harder for female athletes to gain sponsorship and has limited the availability of female sporting role models.
Learning activities
Activity 1: Debate
As a class, hold a debate on the role of women in sport and the restrictions placed on women:
- Why are things still not equal?
- Are there sports that should be men-only or women-only?
- Is it important for young people to have role models?
- Do sports personalities have a responsibility to be or act as role models for their younger fans?
Some sports are designated as women’s or men’s, even though they are very similar. Play a game of basketball, then play a game of netball. Compare the rules and skills needed to play both.
- Is it logical that one is considered a game for men and the other for women?